
Publications
Michalis Nikiforos
-
Working Paper No. 1037 | January 2024The post-pandemic surge in inflation was accompanied by a surge in the corporate share of profits. As a result, several economists and policy makers have given to it names such as “profit-led inflation” or “sellers’ inflation.” The present paper discusses the extent to which profit-led inflation, as an explanation for the recent surge in inflation, is compatible with what we know about the price-setting behavior of firms, income distribution, and inflation. We do that in juxtaposition to two recent critiques: that the increase in the profit share is the result of cyclical factors, and that the increase in import prices leads to higher profit shares even under constant markups. We show that there is little evidence that the recent surge in profitability is cyclical in nature. Moreover, after outlining the Structuralist/Kaleckian theories of prices and inflation we argue that profit-led inflation does not require an increase in the markup of the firms and is consistent with these theories. In the face of large import and other price shocks even under constant markups, firms are able to pass the burden of adjustment to real wages. Thus, the term profit-led emphasizes the distributional source and consequences of inflation. We also provide an empirical examination of the markups in the post-pandemic period using data from the Compustat database. We show that, on average, firms were able to increase or maintain their markups, although there is significant heterogeneity across sectors or the position of the firms in the distribution of markups.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Working Paper No. 1028 | August 2023
Contractionary Effects of Foreign Price Shocks (and Potentially Expansionary Effects of Inflation)
View More View LessUsing the model proposed in Krugman and Taylor’s “Contractionary effects of devaluation” (1978), we examine the macroeconomic effects of shocks to foreign prices. We show that these shocks can be contractionary for two reasons: (i) because they imply a loss of income if an economy has a trade deficit or import prices increase proportionally more than export prices; (ii) because there is a redistribution of income from wages to profits and rent, which leads to a decrease in consumption and output (as the wage earner's propensity to consume is higher than those of profit earners and rentiers). An endogenous reaction of nominal wages to the increase in the price level might lead to even higher increases in prices, but mitigates the negative macroeconomic effects of the foreign price shocks because it reduces their negative distributional effects. If the proportional increase in nominal wages is higher than that of domestic prices, the distributional effect becomes positive. The opposite is the case with markups. If they increase in reaction to higher prices, they contribute to further price increases but they also exacerbate the negative distributional effects. The paper also provides an analytical solution for a general case of the model of Krugman and Taylor. -
Strategic Analysis | July 2023In this Strategic Analysis, Dimitri B. Papadimitriou, Michalis Nikiforos, Giuliano T. Yajima, and Gennaro Zezza discuss how the current state and structural features of the US economy might affect its future trajectory. The recent recovery after the pandemic has been remarkable, when compared to previous cycles, and offers evidence of the efficacy of fiscal policy. Moreover, the inflation rate has been finally decelerating as the problems in global value chains that emerged after the pandemic are resolving and the price of commodities and oil, which spiked after the pandemic and the war in Ukraine, are stabilizing.
Yet despite the recent success of fiscal policy in promoting output and employment growth, the recent debt ceiling deal—culminating in the 2023 Fiscal Responsibility Act—risks putting the US economy on the austerity path of the previous decade. And given the structural weaknesses of the US economy—including its high current account deficits, high level of indebtedness of firms, and overvalued stock and real estate prices—this projected fiscal policy tightening, combined with the impacts of high interest rates, could lead to a significant slowdown of the US economy.
The US economy, the authors contend, is in need of a structural transformation toward modernizing its infrastructure, promoting industrial policy, and investing in the greening of its economy and environmental sustainability. A necessary condition for achieving these goals is an increase in government expenditure; they show that such an increase could also have positive demand effects on output and employment.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | August 2022
The Fed Conundrum
In this report, Institute President Dimitri B. Papadimitriou, Research Scholar Michalis Nikiforos, and Senior Scholar Gennaro Zezza analyze how and why the US economy has achieved a swift recovery in comparison with the last few economic cycles.
This recovery has nevertheless been accompanied by significant increases in the trade deficit and inflation. Papadimitriou, Nikiforos, and Zezza argue that the elevated rate of inflation has been largely unrelated to the level of demand or the pace of the recovery, and has more to do with pandemic-related disruptions, the war in Ukraine, and the beginning of a new commodity super cycle.
The authors also identify persistent Minskyan processes that mean the US economy remains fundamentally unstable, with a risk of financial crisis and potentially severe consequences in terms of output and employment—a risk heightened by the reversal of the loose monetary policy that has prevailed over the last decade and a half. In their first scenario, they simulate the macroeconomic impact of such a financial crisis and private sector deleveraging. In two additional scenarios, the authors analyze the likely effects of a new round of fiscal stimulus that would be necessary in case of a crisis: a deficit-financed expenditure boost with no offsetting revenue increases, and a deficit-neutral scenario in which taxation of high-income households increases by an amount equivalent to the expansion of public expenditure.Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Working Paper No. 1001 | February 2022This paper estimates the distribution-led regime of the US economy for the period 1947–2019. We use a time varying parameter model, which allows for changes in the regime over time. To the best of our knowledge this is the first paper that has attempted to do this. This innovation is important, because there is no reason to expect that the regime of the US economy (or any economy for that matter) remains constant over time. On the contrary, there are significant reasons that point to changes in the regime. We find that the US economy became more profit-led in the first postwar decades until the 1970s and has become less profit-led since; it is slightly wage-led over the last fifteen years.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Paul Carrillo-Maldonado Michalis NikiforosRelated Topic(s):
-
Working Paper No. 993 | September 2021
Theory and Empirics
This paper provides a theoretical and empirical reassessment of supermultiplier theory. First, we show that, as a result of the passive role it assigns to investment, the Sraffian supermultiplier (SSM) predicts that the rate of utilization leads the investment share in a dampened cycle or, equivalently, that a convergent cyclical motion in the utilization-investment share plane would be counterclockwise. Second, impulse response functions from standard recursive vector autoregressions (VAR) for postwar US samples strongly indicate that the investment share leads the rate of utilization, or that these cycles are clockwise. These results raise questions about the key mechanism underlying supermultiplier theory.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | June 2021In this report, Institute President Dimitri B. Papadimitriou and Research Scholars Michalis Nikiforos and Gennaro Zezza analyze how the US economy was affected by the pandemic and its prospects for recovery.
Their baseline simulation using the Institute’s stock-flow macroeconometric model shows a significant pickup in the growth rate in 2021 as a result of the American Rescue Plan Act. The report includes two additional scenarios simulated on top of the baseline, finding that President Biden’s infrastructure and families plans—whether paired with offsetting tax increases on high-earners or “deficit financed”—would have positive macroeconomic effects. Additionally, Papadimitriou, Nikiforos, and Zezza warn that if US policymakers do not prioritize decreasing the trade deficit, maintaining growth will require either continuous and very high government deficits or the private sector once again becoming a net borrower.
Finally, they argue that concerns about a sharp increase in inflation spurred by the fiscal stimulus are unwarranted: the US economy was not close to full employment or full utilization of resources before the pandemic, and the propagation mechanisms that could lead to accelerating inflation are not in place.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 989 | June 2021The paper provides an empirical discussion of the national emergency utilization rate (NEUR), which is based on a “national emergency” definition of potential output and is published by the US Census Bureau. Over the peak-to-peak period 1989–2019, the NEUR decreased by 14.2 percent. The paper examines the trajectory of potential determinants of capacity utilization over the same period as specified in the related theory, namely: capital intensity, relative prices of labor and capital, shift differentials, rhythmic variations in demand, industry concentration, and aggregate demand. It shows that most of them have moved in a direction that would lead to an increase in utilization. The main factor that can explain the decrease in the NEUR is aggregate demand, while the increase in industry concentration might have also played a small role.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Public Policy Brief No. 151 | June 2020
Recent Experience and Future Prospects in the Post-COVID-19 Era
This policy brief provides a discussion of the relationships between austerity, Greece’s macroeconomic performance, debt sustainability, and the provision of healthcare and other social services over the last decade. It explains that austerity was imposed in the name of debt sustainability. However, there was a vicious cycle of recession and austerity: each round of austerity measures led to a deeper recession, which increased the debt-to-GDP ratio and therefore undermined the goal of debt sustainability, leading to another round of austerity. One of the effects of these austerity policies was the significant reduction in healthcare expenditure, which made Greece more vulnerable to the recent pandemic. Finally, it shows how recent pre-COVID debt sustainability analyses projected that Greek public debt would become unsustainable even under minor deviations from an optimistic baseline. The pandemic shock will thus lead to an explosion of public debt. This brings the need for a restructuring of the Greek public debt to the fore once again, as well as other policies that will address the eurozone’s structural imbalances.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | May 2020Greece’s fragile economic recovery was halted by the COVID-19 pandemic: GDP, employment, exports, and investment are expected to record significantly negative trends. While some projections for GDP growth show a quick V-shaped recovery beginning in 2021, this is rather improbable given the Greek economy’s structural inefficiencies.
This strategic analysis explores the consequences of various assumptions about the fall in the different sources of aggregate demand in order to produce a baseline projection for the Greek economy. A more optimistic scenario is also analyzed, in which the European Commission’s recently announced Recovery Fund materializes, allowing the government to increase public consumption as well as investment through EU grants and loans. The authors recommend additional measures to alleviate the impact of the shock and help put Greece’s economy back on track when the epidemic has died out.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 953 | April 2020
Some Empirical Issues
The paper makes three contributions. First, following up on Nikiforos (2016), it provides an in-depth examination of the Federal Reserve measure of capacity utilization and shows that it is closer to a cyclical indicator than a measure of long run variations of normal utilization. Other measures, such as the average workweek of capital or the national emergency utilization rate are more appropriate for examining long-run changes in utilization. Second, and related to that, it argues that a relatively stationary measure of utilization is not consistent with any theory of the determination of utilization. Third, based on data on the lifetime of fixed assets it shows that for the issues around the “utilization controversy” the long run is a period after thirty years or more. This makes it a Platonic Idea for some economic problems.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 952 | April 2020
Some Theoretical Issues
This paper discusses some issues related to the triangle between capital accumulation, distribution, and capacity utilization. First, it explains why utilization is a crucial variable for the various theories of growth and distribution—more precisely, with regards to their ability to combine an autonomous role for demand (along Keynesian lines) and an institutionally determined distribution (along classical lines). Second, it responds to some recent criticism by Girardi and Pariboni (2019). I explain that their interpretation of the model in Nikiforos (2013) is misguided, and that the results of the model can be extended to the case of a monopolist. Third, it provides some concrete examples of why demand is a determinant for the long-run rate of utilization of capital. Finally, it argues that when it comes to the normal rate of utilization, it is the expected growth rate of demand that matters, not the level of demand.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Public Policy Brief No. 149 | April 2020The costs of the COVID-19 pandemic—in terms of both the health risks and economic burdens—will be borne disproportionately by the most vulnerable segments of US society. In this public policy brief, Luiza Nassif-Pires, Laura de Lima Xavier, Thomas Masterson, Michalis Nikiforos, and Fernando Rios-Avila demonstrate that the COVID-19 crisis is likely to widen already-worrisome levels of income, racial, and gender inequality in the United States. Minority and low-income populations are more likely to develop severe infections that can lead to hospitalization and death due to COVID-19; they are also more likely to experience job losses and declines in their well-being.
The authors argue that our policy response to the COVID-19 crisis must target these unequally shared burdens—and that a failure to mitigate the regressive impact of the crisis will not only be unjust, it will prolong the pandemic and undermine any ensuing economic recovery efforts. As the authors note, we are in danger of falling victim to a vicious cycle: the pandemic and economic lockdown will worsen inequality; and these inequalities exacerbate the spread of the virus, not to mention further weaken the structure of the US economy.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Policy Note 2020/1 | March 2020
The Economic Implications of the Pandemic
The spread of the new coronavirus (COVID-19) is a major shock for the US and global economies. Research Scholar Michalis Nikiforos explains that we cannot fully understand the economic implications of the pandemic without reference to two Minskyan processes at play in the US economy: the growing divergence of stock market prices from output prices, and the increasing fragility in corporate balance sheets.
The pandemic did not arrive in the context of an otherwise healthy US economy—the demand and supply dimensions of the shock have aggravated an inevitable adjustment process. Using a Minskyan framework, we can understand how the current economic weakness can be perpetuated through feedback effects between flows of demand and supply and their balance sheet impacts.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
One-Pager No. 61 | March 2020The rapidly growing uncertainty about the potential global fallout from an emerging pandemic is occurring against a background in which there is evidence US corporate sector balance sheets are significantly overstretched, exhibiting a degree of fragility that, according to some measures, is unmatched in the postwar historical record. The US economy is vulnerable to a shock that could trigger a cascade of falling asset prices and private sector deleveraging, with severe consequences for both the real and financial sides of the economy.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Working Paper No. 945 | January 2020
Demand, Distribution, Productivity, Structural Change, and (Secular?) Stagnation
View More View LessThe present paper emphasizes the role of demand, income distribution, endogenous productivity reactions, and other structural changes in the slowdown of the growth rate of output and productivity that has been observed in the United States over the last four decades. In particular, it is explained that weak net export demand, fiscal conservatism, and the increase in income inequality have put downward pressure on demand. Up until the crisis, this pressure was partially compensated for through debt-financed expenditure on behalf of the private sector, especially middle- and lower-income households. This debt overhang is now another obstacle in the way of demand recovery. In turn, as emphasized by the Kaldor-Verdoorn law and the induced technical change approach, the decrease in demand and the stagnation of wages can lead to an endogenous slowdown in productivity growth. Moreover, it is argued that the increasingly oligopolistic and financialized structure of the US economy also contributes to the slowdown. Finally, the paper argues that there is nothing secular about the current stagnation; addressing the aforementioned factors can allow for growth to resume, as has happened in the past.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | January 2020
2020 and Beyond
This Strategic Analysis examines the US economy’s prospects for 2020–23 and the risks that lie ahead. The baseline projection generated by the Levy Institute’s stock-flow consistent macroeconomic model shows that, given current fiscal arrangements and the slowdown in the global economy, the pace of the US recovery will slacken somewhat, with a growth rate that will average 1.5 percent over the next several years.
The authors then point to three factors that can derail this already weak baseline trajectory: (1) an overvalued stock market; (2) evidence that the corporate sector’s balance sheets are more fragile than they have ever been in the postwar period; and (3) risks in the foreign sector stemming from the slowdown of the global economy, an overvalued dollar, and the current administration’s erratic trade policy.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | January 20202019 marked the third year of the continuing economic recovery in Greece, with real GDP and employment rising, albeit at modest rates. In this Strategic Analysis we note that the expansion has mainly been driven by net exports, with tourism playing a dominant role. However, household consumption and investment are still too far below their precrisis levels, and a stronger and sustainable recovery should target these components of domestic demand as well.
Fiscal austerity imposed on the Greek government has achieved its target in terms of public finances, such that some fiscal space is now available to stimulate the economy. Our simulations for the 2019–21 period show that under current conditions the economy is likely to continue on a path of modest growth, and that the amount of private investment needed for a stronger recovery is unlikely to materialize.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 940 | November 2019
A Rejoinder and Some Comments
The critique by Gahn and González (2019) of the conclusions in Nikiforos (2016) regarding what data should be used to evaluate whether capacity utilization is endogenous to demand is weak for the following reasons: (i) The Federal Reserve Board (FRB) measure of utilization is not appropriate for measuring long-run variations of utilization because of the method and purpose of its construction. Even if its difference from the measures of the average workweek of capital (AWW) were trivial, this would still be the case; if anything, it would show that the AWW is also an inappropriate measure. (ii) Gahn and González choose to ignore the longest available estimate of the AWW produced by Foss, which has a clear long-run trend. (iii) Their econometric results are not robust to more suitable specifications of the unit root tests. Under these specifications, the tests overwhelmingly fail to reject the unit root hypothesis. (iv) Other estimates of the AWW, which were not included in Nikiforos (2016) confirm these conclusions. (v) For the comparison between the AWW series and the FRB series, they construct variables that are not meaningful because they subtract series in different units. When the comparison is done correctly, the results confirm that the difference between the AWW series and the FRB series has a unit root. (vi) A stationary utilization rate is not consistent with any theory of the determination of capacity utilization. Even if demand did not play a role, there is no reason to expect that all the other factors that determine utilization would change in a fashion that would keep utilization constant.Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Research Project Reports | September 2019
Macroeconomic and Microeconomic Impacts of Improving Physical and Social Infrastructure
View More View LessA Macro-Micro Policy Model for Ghana and Tanzania
Feminist economics has long emphasized the role of physical and social infrastructure as determinants of the time women spend on household production (the provision of unpaid domestic services and care). Surprisingly, there is a lack of studies that directly investigate how infrastructure improvements affect the time spent on household production and commuting to work, which is another important unpaid activity for most employed individuals. We attempt to fill the lacunae in the research by studying this issue in the context of Ghana and Tanzania utilizing the framework of the Levy Institute Measure of Time and Income Poverty. Separately, while there are several studies (including those done previously at the Levy Institute) on the macroeconomic impacts of government expenditures on care, these assessments tend to be based primarily on employment multipliers along with simple macroeconomic assumptions. We develop a disaggregated and fully articulated macroeconomic model based on the social accounting matrices for the two countries to take account of the intersectoral linkages and external constraints, such as balance of payments, that are particularly important for many developing nations, including Ghana and Tanzania. The macro- and microeconomic aspects are integrated in a unified analytical framework via a top-down disaggregated macroeconomic model with microsimulation that is novel in that it enables the investigation of the gendered economic processes and outcomes at the macroeconomic and microeconomic levels.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Ajit Zacharias Thomas Masterson Fernando Rios-Avila Michalis Nikiforos Kijong Kim Tamar KhitarishviliRelated Topic(s): -
One-Pager No. 60 | July 2019Senators Elizabeth Warren and Bernie Sanders, along with Representative Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, recently proposed to increase the rate of taxation on very high incomes and net worth. One of the primary justifications for such policies is that reducing inequality would help safeguard political equality. However, Dimitri B. Papadimitriou, Michalis Nikiforos, and Gennaro Zezza show how these tax policies, if matched by comparable increases in government spending, have the potential to boost aggregate demand while helping reform the unstable structure of the US economy.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Strategic Analysis | April 2019Although the ongoing recovery is about to become the longest in the history of the United States, it is also the weakest in postwar history, and as we enter the second quarter of 2019, many clouds have gathered.
This Strategic Analysis considers the recent trajectory, the present state, and the future prospects of the US economy. The authors identify four main structural problems that explain how we arrived at the crisis of 2007–09 and why the recovery that has followed has been so weak—as well as why the prospect of a recession is increasingly likely.
The US economy is in need of deep structural reforms that will deal with these problems. This report analyzes a pair of policies that begin to move in that direction, both involving an increase in the tax rate for high-income and high-net-worth households. Even if the primary justification for these policies is not economic, this report shows that if such an increase in taxes is accompanied by an equivalent increase in government outlays, the redistributive impact will have a positive macroeconomic effect while moving the US economy toward a more sustainable future.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 924 | February 2019The paper builds on the concept of (shifting) involvements, originally proposed by Albert
Hirschman (2002 [1982]). However, unlike Hirschman, the concept is framed in class terms. A model is presented where income distribution is determined by the involvement of the two classes, capitalists and workers. Higher involvement by capitalists and lower involvement by workers tends to increase the profit share and vice versa. In turn, shifts in involvements are induced by the potential effect of a change in distribution on economic activity and past levels of distribution. On the other hand, as the profit share increases, the economy tends to become more wage led. The dynamics of the resulting model are interesting. The more the two classes prioritize the increase of their income share over economic activity, the more possible it is that the economy is unstable. Under the stable configuration, the most likely outcome is Polanyian predator-prey cycles, which can explain some interesting historical episodes during the 20th century. Finally, the paper discusses the possibility of conflict and cooperation within each of the distribution-led regimes.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | November 2018The Greek government has managed to exit the stability support program and achieve a higher-than-required primary surplus so as not to require further austerity measures to depress domestic demand. At the same time, the economy has started to recover, mainly due to the good performance of both exports of goods and tourism and modest increases in investment
In this report, we review recent developments in the determinants of aggregate demand and net exports, and provide estimates of two scenarios: one which assumes business as usual and the other an alternate scenario simulating the medium-term impact of an acceleration in investment.
We conclude with a discussion on the sustainability of Greek government debt, showing that it is crucial that the cost of borrowing remains below the nominal growth of national income.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 907 | May 2018
Some Comments on the Sraffian Supermultiplier Approach to Growth and Distribution
View More View LessThe paper discusses the Sraffian supermultiplier (SSM) approach to growth and distribution. It makes five points. First, in the short run the role of autonomous expenditure can be appreciated within a standard post-Keynesian framework (Kaleckian, Kaldorian, Robinsonian, etc.). Second, and related to the first, the SSM model is a model of the long run and has to be evaluated as such. Third, in the long run, one way that capacity adjusts to demand is through an endogenous adjustment of the rate of utilization. Fourth, the SSM model is a peculiar way to reach what Garegnani called the “Second Keynesian Position.” Although it respects the letter of the “Keynesian hypothesis,” it makes investment quasi-endogenous and subjects it to the growth of autonomous expenditure. Fifth, in the long run it is unlikely that “autonomous expenditure” is really autonomous. From a stock-flow consistent point of view, this implies unrealistic adjustments after periods of changes in stock-flow ratios. Moreover, if we were to take this kind of adjustment at face value, there would be no space for Minskyan financial cycles. This also creates serious problems for the empirical validation of the model.Download:Associated Program(s):The State of the US and World Economies Monetary Policy and Financial Structure Explorations in Theory and Empirical AnalysisAuthor(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | April 2018The US economy has been expanding continuously for almost nine years, making the current recovery the second longest in postwar history. However, the current recovery is also the slowest recovery of the postwar period.
This Strategic Analysis presents the medium-run prospects, challenges, and contradictions for the US economy using the Levy Institute’s stock-flow consistent macroeconometric model. By comparing a baseline projection for 2018–21 in which no budget or tax changes take place to three additional scenarios, the authors isolate the likely macroeconomic impacts of: (1) the recently passed tax bill; (2) a large-scale public infrastructure plan of the same “fiscal size” as the tax cuts; and (3) the spending increases entailed by the Bipartisan Budget Act and omnibus bill. Finally, Nikiforos and Zezza update their estimates of the likely outcome of a scenario in which there is a sharp drop in the stock market that induces another round of private-sector deleveraging.
Although in the near term the US economy could see an acceleration of its GDP growth rate due to the recently approved increase in federal spending and the new tax law, it is increasingly likely that the recovery will be derailed by a crisis that will originate in the financial sector.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 891 | May 2017
A Survey
The stock-flow consistent (SFC) modeling approach, grounded in the pioneering work of Wynne Godley and James Tobin in the 1970s, has been adopted by a growing number of researchers in macroeconomics, especially after the publication of Godley and Lavoie (2007), which provided a general framework for the analysis of whole economic systems, and the recognition that macroeconomic models integrating real markets with flow-of-funds analysis had been particularly successful in predicting the Great Recession of 2007–9. We introduce the general features of the SFC approach for a closed economy, showing how the core model has been extended to address issues such as financialization and income distribution. We next discuss the implications of the approach for models of open economies and compare the methodologies adopted in developing SFC empirical models for whole countries. We review the contributions where the SFC approach is being adopted as the macroeconomic closure of microeconomic agent-based models, and how the SFC approach is at the core of new research in ecological macroeconomics. Finally, we discuss the appropriateness of the name “stock-flow consistent” for the class of models we survey.
Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | April 2017From a macroeconomic point of view, 2016 was an ordinary year in the post–Great Recession period. As in prior years, the conventional forecasts predicted that this would be the year the economy would finally escape from the “new normal” of secular stagnation. But just as in every previous year, the forecasts were confounded by the actual result: lower-than-expected growth—just 1.6 percent.
The radical policy changes promoted by the new Trump administration dominated economic conditions in the closing quarter of the year and the first quarter of 2017. Markets have responded with exuberance since the November elections, on the expectation that the proposed policy measures would increase profitability by boosting growth and cutting personal and corporate taxes. However, an evaluation of the US economy’s structural characteristics reveals three key impediments to a robust, sustainable recovery: income inequality, fiscal conservatism, and weak net export demand. The new administration’s often conflicting policy proposals are unlikely to solve any of these fundamental problems—if anything, the situation will worsen.
Our latest Strategic Analysis provides two medium-term scenarios for the US economy. The “business as usual” baseline scenario (built on CBO estimates) shows household debt and GDP growth roughly maintaining their moribund postcrisis trends. The second scenario assumes a sharp correction in the stock market beginning in 2017Q3, combined with another round of private sector deleveraging. The results: negative growth and a government deficit of 8.3 percent by 2020—essentially a repeat of the crisis of 2007–9.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 879 | December 2016
This paper presents a methodological discussion of two recent “endogeneity” critiques of the Kaleckian model and the concept of distribution-led growth. From a neo-Keynesian perspective, and following Kaldor (1955) and Robinson (1956), the model is criticized because it treats distribution as quasi-exogenous, while in Skott (2016) distribution is viewed as endogenously determined by a series of (exogenous) institutional factors and social norms, and therefore one should focus on these instead of the functional distribution of income per se. The paper discusses how abstraction is used in science and economics, and employs the criteria proposed by Lawson (1989) for what constitutes an appropriate abstraction. Based on this discussion, it concludes that the criticisms are not valid, although the issues raised by Skott provide some interesting directions for future work within the Kaleckian framework.
Download:Associated Program(s):Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | October 2016
The Greek government has agreed to a new round of fiscal austerity measures consisting of a sharp increase in taxes on income and property and further reductions in pension and other welfare-related expenditures. Based on our model of the Greek economy, policies aimed at reducing the government deficit will cause a recession, unless other components of aggregate demand increase enough to more than offset the negative impact of fiscal austerity on output and employment.
In this report we argue that the troika strategy of increasing net exports to restart the economy has failed, partly because of the low impact of falling wages on prices, partly because of the low trade elasticities with respect to prices, and partly because of other events that caused a sharp reduction in transport services, which used to be Greece’s largest export sector.
A policy initiative to boost aggregate demand is urgently needed, now more than ever. We propose a fiscal policy alternative based on innovative financing mechanisms, which could trigger a boost in confidence that would encourage renewed private investment.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 867 | May 2016
This paper examines the issue of the Greek public debt from different perspectives. We provide a historical discussion of the accumulation of Greece’s public debt since the 1960s and the role of public debt in the recent crisis. We show that the austerity imposed since 2010 has been unsuccessful in stabilizing the debt while at the same time taking a heavy toll on the Greek economy and society. The experience of the last six years shows that the country’s public debt is clearly unsustainable, and therefore a bold restructuring is needed. An insistence on the current policies is not justifiable either on pragmatic or on moral or any other grounds. The experience of Germany in the early post–World War II period provides some useful hints for the way forward. A solution to the Greek public debt problem is a necessary but not sufficient condition for the solution of the Greek and wider European crisis. A broader agenda that deals with the malaises of the Greek economy and the structural imbalances of the eurozone is of vital importance.
Download:Associated Program(s):The State of the US and World Economies Monetary Policy and Financial Structure Economic Policy for the 21st CenturyAuthor(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | March 2016Our latest strategic analysis reveals that the US economy remains fragile because of three persistent structural issues: weak demand for US exports, fiscal conservatism, and a four-decade trend in rising income inequality. It also faces risks from stagnation in the economies of the United States’ trading partners, appreciation of the dollar, and a contraction in asset prices. The authors provide a baseline and three alternative medium-term scenarios using the Levy Institute’s stock-flow consistent macro model: a dollar appreciation and reduced growth in US trading partners scenario; a stock market correction scenario; and a third scenario combining scenarios 1 and 2. The baseline scenario shows that future growth will depend on an increase in private sector indebtedness, while the remaining scenarios underscore the linkages between a fragile US recovery and instability in the global economy.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
One-Pager No. 52 | January 2016
Even under optimistic assumptions, the policy status quo being enforced in Greece cannot be relied upon to help recover lost incomes and employment within any reasonable time frame. And while a widely discussed public investment program funded by European institutions would help, a more innovative, better-targeted solution is required to address Greece’s protracted unemployment crisis: an “employer of last resort” (ELR) plan offering paid work in public projects, financed by issuing a nonconvertible “fiscal currency”—the Geuro.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | January 2016The Greek economy has not succeeded in restoring growth, nor has it managed to restore a climate of reduced uncertainty, which is crucial for stabilizing the business climate and promoting investment. On the contrary, the new round of austerity measures that has been agreed upon implies another year of recession in 2016.
After reviewing some recent indicators for the Greek economy, we project the trajectory of key macroeconomic indicators over the next three years. Our model shows that a slow recovery can be expected beginning in 2017, at a pace that is well below what is needed to alleviate poverty and reduce unemployment. We then analyze the impact of a public investment program financed by European institutions, of a size that is feasible given the current political and economic conditions, and find that, while such a plan would help stimulate the economy, it would not be sufficient to speed up the recovery. Finally, we revise our earlier proposal for a fiscal stimulus financed through the emission of a complementary currency targeted to job creation. Our model shows that such a plan, calibrated in a way that avoids inflationary pressures, would be more effective—without disrupting the targets the government has agreed upon in terms of its primary surplus, and without reversing the improvement in the current account.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 844 | July 2015
We present a model where the saving rate of the household sector, especially households at the bottom of the income distribution, becomes the endogenous variable that adjusts in order for full employment to be maintained over time. An increase in income inequality and the current account deficit and a consolidation of the government budget lead to a decrease in the saving rate of the household sector. Such a process is unsustainable because it leads to an increase in the household debt-to-income ratio, and maintaining it depends on some sort of asset bubble. This framework allows us to better understand the factors that led to the Great Recession and the dilemma of a repeat of this kind of unsustainable process or secular stagnation. Sustainable growth requires a decrease in income inequality, an improvement in the external position, and a relaxation of the fiscal stance of the government.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | May 2015
The Greek economy has the potential to recover, and in this report we argue that access to alternative financing sources such as zero-coupon bonds (“Geuros”) and fiscal credit certificates could provide the impetus and liquidity needed to grow the economy and create jobs. But there are preconditions: the existing government debt must be rolled over and austerity policies put aside, restoring trust in the country’s economic future and setting the stage for sustainable income growth, which will eventually enable Greece to repay its debt.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | May 2015
Fiscal Austerity, Dollar Appreciation, and Maldistribution Will Derail the US Economy
View More View LessIn this latest Strategic Analysis, the Institute’s Macro Modeling Team examines the current, anemic recovery of the US economy. The authors identify three structural obstacles—the weak performance of net exports, a prevailing fiscal conservatism, and high income inequality—that, in combination with continued household sector deleveraging, explain the recovery’s slow pace. Their baseline macro scenario shows that the Congressional Budget Office’s latest GDP growth projections require a rise in private sector spending in excess of income—the same unsustainable path that preceded both the 2001 recession and the Great Recession of 2007–9. To better understand the risks to the US economy, the authors also examine three alternative scenarios for the period 2015–18: a 1 percent reduction in the real GDP growth rate of US trading partners, a 25 percent appreciation of the dollar over the next four years, and the combined impact of both changes. All three scenarios show that further dollar appreciation and/or a growth slowdown in the trading partner economies will lead to an increase in the foreign deficit and a decrease in the projected growth rate, while heightening the need for private (and government) borrowing and adding to the economy’s fragility.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Policy Note 2015/2 | February 2015
The Greek economic crisis started as a public debt crisis five years ago. However, despite austerity and a bold “haircut,” public debt is now around 175 percent of Greek GDP. In this policy note, we argue that Greece’s public debt is clearly unsustainable, and that a significant restructuring of this debt is needed in order for the Greek economy to start growing again. Insistence on maintaining the current policy stance is not justifiable on either pragmatic or moral grounds.
The experience of Germany in the early post–World War II period provides some useful insights for the way forward. In the aftermath of the war, there was a sweeping cancellation of the country’s public and foreign debt, which was part of a wider plan for the economic and political reconstruction of Germany and Europe. Seven decades later, while a solution to the unsustainability of the Greek public debt is a necessary condition for resolving the Greek and European crisis, it is not, in itself, sufficient. As the postwar experience shows, a broader agenda that deals with both Greece’s domestic economic malaise and the structural imbalances in the eurozone is also of vital importance.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | December 2014With the anti-austerity Syriza party continuing to lead in polls ahead of Greece’s election on January 25, what is the outlook for restoring growth and increasing employment following six years of deep recession?Despite some timid signs of recovery, notably in the tourism sector, recent short-term indicators still show a decline for 2014. Our analysis shows that the speed of a market-driven recovery would be insufficient to address the urgent problems of poverty and unemployment. And the protracted austerity required to service Greece’s sovereign debt would merely ensure the continuation of a national crisis, with spillover effects to the rest of the eurozone—especially now, when the region is vulnerable to another recession and a prolonged period of Japanese-style price deflation.Using the Levy Institute’s macroeconometric model for Greece, we evaluate the impact of policy alternatives aimed at stimulating the country’s economy without endangering its current account, including capital transfers from the European Union, suspension of interest payments on public debt and use of these resources to boost demand and employment, and a New Deal plan using public funds to target investment in production growth and finance a direct job creation program.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Working Paper No. 814 | September 2014
The paper examines the long-run fluctuations in growth and distribution through the prism of wage-and profit-led growth. We argue that the relation between distribution of income and growth changes over time. We propose an endogenous mechanism that leads to fluctuations between wage- and profit-led periods. Our model is a linear version of Goodwin’s predator–prey model, but with a reversal of the roles for predator and prey: the growth rate acts as the predator and the distribution of income as the prey. These fluctuations need to be taken into account when someone estimates empirically the effect of a change in distribution on utilization and growth. We also examine our argument in relation to the double movement of Karl Polanyi, the Kuznets curve, and the theories of long swings proposed by Albert Hirschman and Michal Kalecki.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | August 2014What are the prospects for economic recovery if Greece continues to follow the troika strategy of fiscal austerity and internal devaluation, with the aim of increasing competitiveness and thus net exports? Our latest strategic analysis indicates that the unprecedented decline in real and nominal wages may take a long time to exert its effects on trade—if at all—while the impact of lower prices on tourism will not generate sufficient revenue from abroad to meet the targets for a surplus in the current account that outweighs fiscal austerity. The bottom line: a shift in the fiscal policy stance, toward lower taxation and job creation, is urgently needed.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Strategic Analysis | April 2014The US economy has been expanding moderately since the official end of the Great Recession in 2009. The budget deficit has been steadily decreasing, inflation has remained in check, and the unemployment rate has fallen to 6.7 percent. The restrictive fiscal policy stance of the past three years has exerted a negative influence on aggregate demand and growth, which has been offset by rising domestic private demand; net exports have had only a negligible (positive) effect on growth.As Wynne Godley noted in 1999, in the Strategic Analysis Seven Unsustainable Processes, if an economy faces sluggish net export demand and fiscal policy is restrictive, economic growth becomes dependent on the private sector’s continuing to spend in excess of its income. However, this continuous excess is not sustainable in the medium and long run. Therefore, if spending were to stop rising relative to income, without either fiscal relaxation or a sharp recovery in net exports, the impetus driving the expansion would evaporate and output could not grow fast enough to stop unemployment from rising. Moreover, because growth is so dependent on “rising private borrowing,” the real economy “is at the mercy of the stock market to an unusual extent.” As proved by the crisis of 2001 and the Great Recession of 2007–09, Godley’s analysis turned out to be correct.Fifteen years later, the US economy appears to be going down the same road again. Postrecession, foreign demand is still weak and the government is maintaining its tight fiscal stance. Once again, the recovery predicted in the latest Congressional Budget Office report relies on excessive private sector borrowing, and once again, the recovery is at the mercy of the stock market. Given that the income distribution has worsened since the crisis—continuing a 35-year trend—the burden of indebtedness will again fall disproportionally on the middle class and the poor. In order for the CBO projections to materialize, households in the bottom 90 percent of the distribution would have to start accumulating debt again in line with the prerecession trend while the stock of debt of the top 10 percent remained at its present level. Clearly, this process is unsustainable. The United States now faces a choice between two undesirable outcomes: a prolonged period of low growth—secular stagnation—or a bubble-fueled expansion that will end with a serious financial and economic crisis. The only way out of this dilemma is a reversal of the trend toward greater income inequality.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Strategic Analysis | February 2014In this report, we discuss alternative scenarios for restoring growth and increasing employment in the Greek economy, evaluating alternative policy options through our specially constructed macroeconometric model (LIMG). After reviewing recent events in 2013 that confirm our previous projections for an increase in the unemployment rate, we examine the likely impact of four policy options: (1) external help through Marshall Plan–type capital transfers to the government; (2) suspension of interest payments on public debt, instead using these resources for increasing demand and employment; (3) introduction of a parallel financial system that uses new government bonds; and (4) adoption of an employer-of-last-resort (ELR) program financed through the parallel financial system. We argue that the effectiveness of the different plans crucially depends on the price elasticity of the Greek trade sector. Since our analysis shows that such elasticity is low, our ELR policy option seems to provide the best strategy for a recovery, having immediate effects on the Greek population's standard of living while containing the effects on foreign debt.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Strategic Analysis | October 2013If the Congressional Budget Office’s recent projections of government revenues and outlays come to pass, the United States will not grow fast enough to bring down the unemployment rate between now and 2016. The public sector deficit will decline from present levels, endangering the sustainability of the recovery. But as this new Strategic Analysis shows, a public sector stimulus of a little over 1 percent of GDP per year focused on export-oriented R & D investment would increase US competitiveness through export-price effects, resulting in a rise of net exports, and slowly lower unemployment to less than 5 percent by 2016. The improvement in net export demand would allow the US economy to enter a period of aggregate-demand rehabilitation—with very encouraging consequences at home.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
-
Policy Note 2013/9 | October 2013
A Scenario of Hitting the Debt Ceiling
The United States entered the second week of a government shutdown on Monday, with no end to the deadlock in sight. The cost to the government of a similar shutdown in 1995–96 amounted to $2.1 billion in today’s dollars. However, the cost and broader consequences of today’s shutdown are not yet clear—especially since the US economy is in the midst of an anemic recovery from the biggest economic crisis of the last eight decades.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
One-Pager No. 41 | September 2013
Why the Troika’s Greek Strategy Is Failing
Greece’s unemployment rate just hit 27.6 percent. That wasn’t supposed to happen. Why has the troika—the European Commission, International Monetary Fund (IMF), and European Central Bank—been so consistently wrong about the effects of its handpicked policies? The strategy being imposed on Greece depends in large part on the idea of “internal devaluation”: that reducing wages will make its products more attractive, thus spurring a return to economic growth powered by rising exports. Our research, based on a macroeconomic model specifically constructed for Greece, indicates that this strategy is not working. Achieving significant growth in net exports through internal devaluation would, at best, take a very long time—and a great deal of immiseration and social disintegration would take place while we waited for this theory to bear fruit. Despite some recent admissions of error along these lines by the IMF, the troika still relies on a theory of how the economy works that badly underestimates the negative effects of austerity.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 771 | August 2013
In Search of Causality
This paper analyzes the trajectories of the Greek public deficit and sovereign debt over the last three decades and their connection to the political and economic environment, paying special attention to the causality between the public and the foreign deficit. The authors argue that, from 1980 to 1995, causality ran from the public deficit to the foreign deficit but has since reversed, a result of the European monetary unification process and the adoption of the common currency. This hypothesis is tested and verified econometrically using the Granger causality and cointegration analyses.Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Working Paper No. 770 | July 2013
An Essay on the Business Cycle
This paper presents a discussion of the forces at play behind the economic fluctuations in the medium run and their relation with the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium. The business cycle is the result of two separate phenomena. On the one hand, there is the instability caused by the discrepancy between expected and realized outcomes. On the other hand, this instability is contained by the inherent contradictions of capitalism; the upswing carries within it “the seeds of its own destruction.” The same happens with the downswing. The paper provides a formal exposition of these insights, a discussion of how the formulation of this mechanism resembles the simple harmonic motion of classical mechanics, and an empirical evaluation.Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Research Project Reports | July 2013
Technical Paper
In this report Levy Institute President Dimitri B. Papadimitriou and Research Scholars Gennaro Zezza and Michalis Nikiforos present the technical structure of the Levy Institute's macroeconomic model for the Greek economy (LIMG). LIMG is a stock-flow consistent model that reflects the “New Cambridge” approach that builds on the work of Distinguished Scholar Wynne Godley and the current Levy Institute model for the US economy. LIMG is a flexible tool for the analysis of economic policy alternatives for the medium term and is also the analytic framework for a forthcoming Strategic Analysis series focusing on the Greek economy.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Strategic Analysis | July 2013
A Strategic Analysis
Employment in Greece is in free fall, with more than one million jobs lost since October 2008—a drop of more than 28 percent. In March, the “official” unemployment rate was 27.4 percent, the highest level seen in any industrialized country in the free world during the last 30 years.
In this report, Levy Institute President Dimitri B. Papadimitriou and Research Scholars Michalis Nikiforos and Gennaro Zezza present their analysis of Greece’s economic crisis and offer policy recommendations to restore growth and increase employment. This analysis relies on the Levy Institute’s macroeconomic model for the Greek economy (LIMG), a stock-flow consistent model similar to the Institute’s model of the US economy. Based on the LIMG simulations, the authors find that a continuation of “expansionary austerity” policies will actually increase unemployment, since GDP will not grow quickly enough to arrest, much less reverse, the decline in employment. They critically evaluate recent International Monetary Fund and European Commission projections for the Greek economy, and find these projections overly optimistic. They recommend a recovery plan, similar to the Marshall Plan, to increase public consumption and investment. Toward this end, the authors call for an expanded direct public-service job creation program.Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Policy Note 2013/3 | April 2013
This policy note discusses the prospects for job creation in the US based on the most recent Levy Economics Institute Strategic Analysis report, Is the Link between Jobs and Output Broken? The results of our analysis confirm the continued weakness of the US economy in terms of job creation—a phenomenon that has come to be known as a “jobless recovery.” We argue that to understand the problem we must look beyond the unemployment rate, which can conceal changes in the labor force. A prolonged recession can discourage workers, causing them to drop out of the labor market, thus lowering the unemployment rate without increasing employment. Therefore, the total number of people employed should be considered in tandem with the unemployment rate.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s): -
Strategic Analysis | March 2013
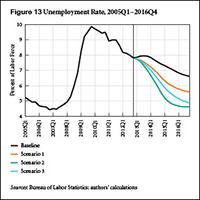
As this report goes to press, the official unemployment rate remains tragically elevated, compared even to rates at similar points in previous recoveries. The US economy seems once again to be in a “jobless recovery,” though the unemployment rate has been steadily declining for years. At the same time, fiscal austerity has arrived, with the implementation of the sequester cuts, following tax increases and the ending of emergency extended unemployment benefits just two months ago.
Our new report provides medium-term projections of employment and economic growth under four different scenarios. The baseline scenario starts by assuming the same growth rates and government deficits as the Congressional Budget Office’s (CBO) baseline projection from earlier this year. The result is a new surge of the unemployment rate to nearly 8 percent in the third quarter of this year, followed by a very gradual new recovery. Scenarios 1 and 2 seek to reach unemployment-rate goals of 6.5 percent and 5.5 percent, respectively, by the end of next year, using new fiscal stimulus.
We find in these simulations that reaching the goals requires large amounts of fiscal stimulus, compared to the CBO baseline. For example, in order to reach 5.5 percent unemployment in 2014, scenario 2 assumes 11 percent growth in inflation-adjusted government spending and transfers, along with lower taxes.
As an alternative, scenario 3 adds an extra increase to growth abroad and to private borrowing, along with the same amount of fiscal stimulus as in scenario 1. In this last scenario of the report, the unemployment rate finally pierces the 5.5 percent threshold from the previous scenario in the third quarter of 2015. We conclude with some thoughts about how such an increase in demand from all three sectors—government, private, and external—might be realistically obtained.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 739 | November 2012
A Theoretical and Empirical Discussion of the Kaleckian Model of Growth and Distribution
This paper examines the “utilization controversy” around the Kaleckian model of growth and distribution. We show that the Federal Reserve data on capacity utilization, which have been used by both sides of this debate, are the wrong kind of data for the issue under examination. Instead, a more appropriate measurement can be derived from the data on the Average Workweek of Capital. We argue that the long-run dynamic adjustment proposed by Kaleckian scholars lacks a coherent economic rationale, and provide an alternative path toward the endogeneity of the desired utilization at the micro and macro levels. Finally, we examine the proposed adjustment mechanism econometrically. Our results verify the endogeneity of the normal utilization rate.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s): -
Working Paper No. 737 | November 2012
This paper examines the endogeneity (or lack thereof) of the rate of capacity utilization in the long run at the firm level. We provide economic justification for the adjustment of the desired rate of utilization toward the actual rate on behalf of a cost-minimizing firm after examining the factors that determine the utilization of resources. The cost-minimizing firm has an incentive to increase the utilization of its capital if the rate of the returns to scale decreases as its production increases. The theory of economies of scale provides justification for this kind of behavior. In this manner, the desired rate of utilization becomes endogenous.
Download:Associated Program:Author(s):Related Topic(s):
